RTIL Nanoparticle Dispersion and Graphite Exfoliation for Nanocomposites
James Throckmorton, Ph.D. CandidateRTILs for Nanoparticle Dispersion and Polymer Initiation
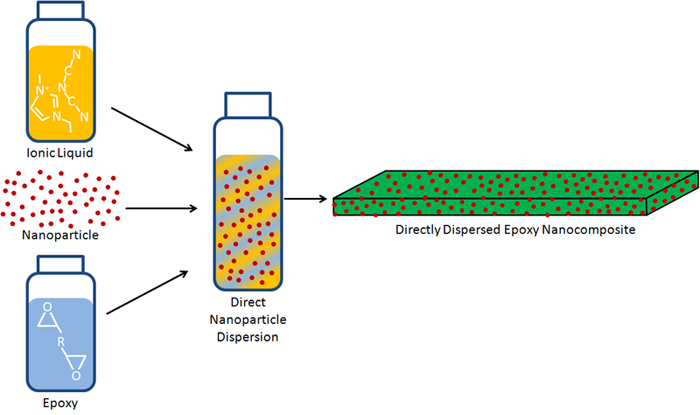
Nanocomposite processing can be simplified by the use of the same compound as both a nanoparticle solvent and an initiator for polymerization. This dual-function molecule can be designed both for solvent potential and reaction chemistry. EMIM-DCN, previously shown by our lab to act as an epoxy initiator, is used in the synthesis of silica and acid expanded graphitecomposites. These composites are then characterized for particle dispersion and physical properties. Individual particle dispersion of silica nanocomposites is shown by DLS and SEM, and silica nanocomposites at low loading show individual particle dispersion and improved modulus and fracture toughness. GNP nanocomposites show a 70% increase in modulus along with a 10-order of magnitude increase in electrical conductivity at 6.5 vol%, and an electrical percolation threshold of 1.7 vol%.
Direct Graphite Nanocomposites By Laminar Shear Exfoliation and RTIL Dispersion
This work presents an laminar-shear alternative to chemical processing and chaotic flow-fields for the direct exfoliation of graphite and the single-pot preparaton of nanocomposites. Additionally, we develop the theory of laminar flow through a 3-roll mill, and apply that theory to the latest developments in the theory of graphite interlayer shear. The resulting nanocomposite shows low electrical percolation (0.5 vol%) and low thickness (1-3 layer) graphite/graphene flakes by TEM. Additionally, the effect of processing conditions by rheometry and comparison with solvent-free conditions reveal the interactions between processing and matrix properties and provide insight into the theory of the chemical and physical exfoliation of graphite crystals and the resulting polymer matrix dispersion.

Relevant Publications
"Room Temperature Ionic Liquids for Epoxy Nanocomposite Synthesis: Direct dispersion and cure" Throckmorton, JA; Watters, AL; Geng, X; Palmese, GR; Composites Science and Technology Vol. 86 pp. 38-44 (2013) .
"Hydrolytic Degradation of Highly Crosslinked Polyaromatic Cyanate Ester Resins" Marella, V; Throckmorton, JA; Palmese, GR Vol. 104, pp. 104-111 (2014)
Back to Main Research Page


