Investigating the Effect of Network Structure/Topology on Mechanical Properties
of Crosslinked Polymers
Majid Sharifi, Ph.D. Candidate
A new approach on toughening epoxy material is presented. The idea, unlike other conventions, is primarily focusing on the topological structure of the polymer networks and explore the possibility of manipulating the material's properties (mechanical, physical and transport prop.) without sacrificing thermal stability and glass transition temperature.
The concept of topology-based toughening will provide a better understanding of the new generation of thermosetting materials that can be tailored based on the end-application where materials with specific enhanced physical, mechanical and transport properties are preferred. The polymer network with altered topology will enable us to produce more sustainable protective coatings, structural materials and high performance composites.
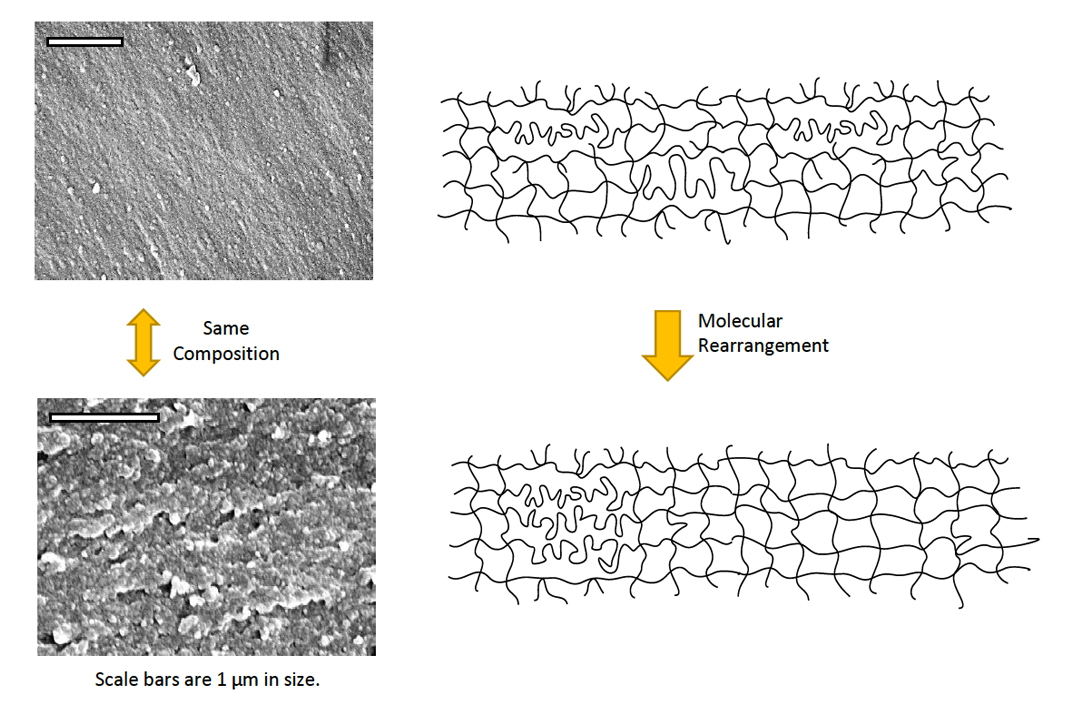
Figure 1. The micrographs are showing the room-temperature fracture surface of the two epoxy network isomers with rearranged molecular structures. The schematics on the left are showing the probable molecular structure.
Relevant Publications
M. Sharifi, G.R. Palmese, "Toughened Epoxy Materials via Incorporation of Partially-Reacted Substructures; Synthesis and Characterization", in progress.
M. Sharifi, K.A. Ghorpade, V.I. Raman, G.R. Palmese, "Analysis of Epoxy Network Structures through Polymer Swelling Behavior", in progress.
M. Sharifi, C. W. Jang, C. Abrams and G. R. Palmese, Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014.
C. Jang, M. Sharifi, G. R. Palmese and C. F. Abrams, Polymer, 2014, 55, 3859-3868.
P. A. Pratama, M. Sharifi, A. M. Peterson and G. R. Palmese, ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2013, 5, 12425-12431.
Back to Main Research Page


